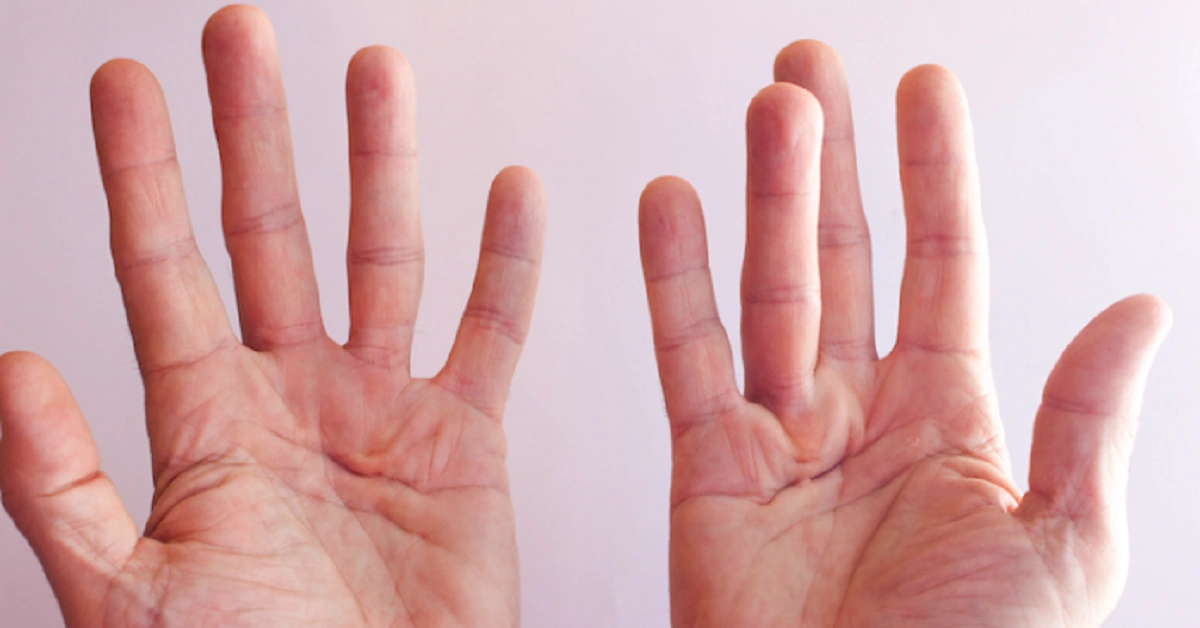
Loguytren problems, often referred to in connection with Dupuytren’s contracture, represent a significant challenge for individuals experiencing this condition. It involves the thickening of connective tissues in the hands, resulting in restricted finger movements and limited hand functionality. This condition primarily targets the palms, leading to nodules and contractures that hinder basic tasks such as gripping objects or shaking hands. Despite its non-life-threatening nature, the impact on daily life and personal independence can be profound, necessitating a deeper understanding of its causes, symptoms, and available treatments. By exploring these aspects, individuals can gain actionable insights to manage and mitigate the effects of Loguytren problems.
Understanding Loguytren Problems
Loguytren problems are characterized by the progressive thickening of the palmar fascia—a layer of connective tissue located beneath the skin of the palm. Over time, this thickening can cause the fingers to curl inward, creating a claw-like appearance. While the exact mechanisms remain under investigation, studies suggest that genetic and environmental factors contribute significantly to its onset. Often confused with arthritis or other joint disorders, Loguytren problems are unique in their focus on soft tissues rather than bone or cartilage.
This condition predominantly affects individuals of Northern European descent and is more common in men than women. While it often manifests after the age of 40, younger individuals are not entirely immune. The gradual progression, coupled with varying degrees of severity, underscores the importance of early detection and intervention. By understanding the defining characteristics of Loguytren problems, individuals can seek timely medical advice to address the condition effectively.
Causes of Loguytren Problems
The causes of Loguytren problems are multifaceted, involving a combination of genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors. One of the primary contributors is heredity; individuals with a family history of the condition are significantly more likely to develop it themselves. Beyond genetics, age and gender also play crucial roles, with older men being the most commonly affected demographic.
Environmental factors such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been shown to exacerbate the condition. These habits may influence the vascular and cellular health of connective tissues, accelerating the development of nodules and contractures. Additionally, underlying health conditions like diabetes and epilepsy are associated with an increased risk of Loguytren problems. While these factors do not guarantee the onset of the condition, they collectively contribute to its likelihood and progression.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing Symptoms
The early signs of Loguytren problems often include subtle changes in the palm’s skin texture. These may present as small lumps or nodules that feel firm to the touch. Over time, these nodules can develop into thickened cords that pull the fingers inward, leading to a claw-like hand posture. The most commonly affected fingers are the ring and pinky fingers, though the condition can extend to other digits in advanced stages.
As the condition progresses, individuals may experience pain, though this is not a universal symptom. The loss of hand mobility and flexibility becomes increasingly apparent, interfering with daily activities such as writing, typing, and gripping objects. For many, the psychological toll of losing independence in routine tasks can be as impactful as the physical symptoms themselves.
Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosing Loguytren problems involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. During a physical examination, the doctor will assess the appearance and mobility of the affected hand, focusing on the presence of nodules and skin thickening. Functional tests, such as the table-top test, are often used to determine the extent of finger contractures. In some cases, imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI may be employed to gain a deeper understanding of the affected tissues, though these are generally reserved for complex cases. Early diagnosis is critical for devising an effective treatment plan that minimizes long-term complications.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with Loguytren problems can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Simple activities such as buttoning a shirt, shaking hands, or holding a cup of coffee become increasingly challenging as the condition progresses. Beyond the physical limitations, many individuals experience emotional distress stemming from their reduced independence and altered self-image. The condition can also impact professional life, particularly for those in occupations requiring fine motor skills or repetitive hand movements.
For caregivers and family members, supporting someone with Loguytren problems requires patience and understanding. Encouraging the use of assistive devices, arranging physical therapy sessions, and offering emotional support are essential aspects of holistic care. By addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by the condition, individuals and their families can work towards maintaining a higher quality of life.
Progression of the Condition
Loguytren problems are typically progressive, with symptoms worsening over months or years. The initial phase often involves minor discomfort and mild contractures that may not interfere significantly with daily life. However, as the condition advances, the affected fingers may become permanently curled, leading to a significant loss of hand functionality. In severe cases, individuals may be unable to perform even basic tasks, such as tying shoelaces or cooking meals.
Understanding the typical progression of Loguytren problems can help individuals and healthcare providers develop proactive management strategies. Regular monitoring and early intervention can slow the condition’s progression and improve overall outcomes.
Exploring Treatment Options
Physical Therapy and Lifestyle Adjustments
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of managing Loguytren problems. Stretching exercises designed to improve finger flexibility and maintain range of motion are particularly effective in the early stages. Therapists often recommend using stress balls, grip-strengthening tools, and specialized splints to prevent further contractures.
Lifestyle adjustments, such as avoiding repetitive hand strain and quitting smoking, can also play a crucial role in slowing disease progression. Adopting a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may further support connective tissue health, though more research is needed in this area.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For individuals with moderate symptoms, minimally invasive treatments offer promising results with shorter recovery times. Collagenase injections, for example, use enzymes to break down thickened tissue, allowing for improved finger extension. Needle aponeurotomy is another effective option, involving the use of a fine needle to release tightened cords under the skin. Both procedures are outpatient treatments, enabling patients to return to their normal routines quickly.
Surgical Interventions
In advanced cases, surgery may be the most viable option for restoring hand functionality. Procedures such as fasciectomy and dermofasciectomy involve the removal of affected tissues, with the latter often incorporating skin grafts to reduce recurrence risk. While surgical interventions generally offer long-term relief, they require a more extended recovery period and may carry risks such as infection or scarring.
Preventive Strategies
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Preventing Loguytren problems involves adopting habits that promote overall hand health. Regular hand exercises, avoiding repetitive strain, and maintaining optimal blood sugar levels are essential steps. For those with a family history of the condition, early monitoring and lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the risk of severe progression.
Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol consumption are particularly important, as both habits have been linked to an increased likelihood of developing Loguytren problems. By prioritizing preventive measures, individuals can minimize the impact of this condition on their lives.
Future Research and Advancements
Ongoing research into Loguytren problems is paving the way for innovative treatments. Promising areas of study include stem cell therapies, which aim to regenerate damaged connective tissues, and gene-editing techniques that target the genetic underpinnings of the condition. Additionally, advancements in surgical tools and techniques are making procedures less invasive and recovery periods shorter.
As our understanding of the condition deepens, the medical community is optimistic about developing more effective and accessible treatments. These advancements hold the potential to transform the way Loguytren problems are managed, offering hope to those affected.